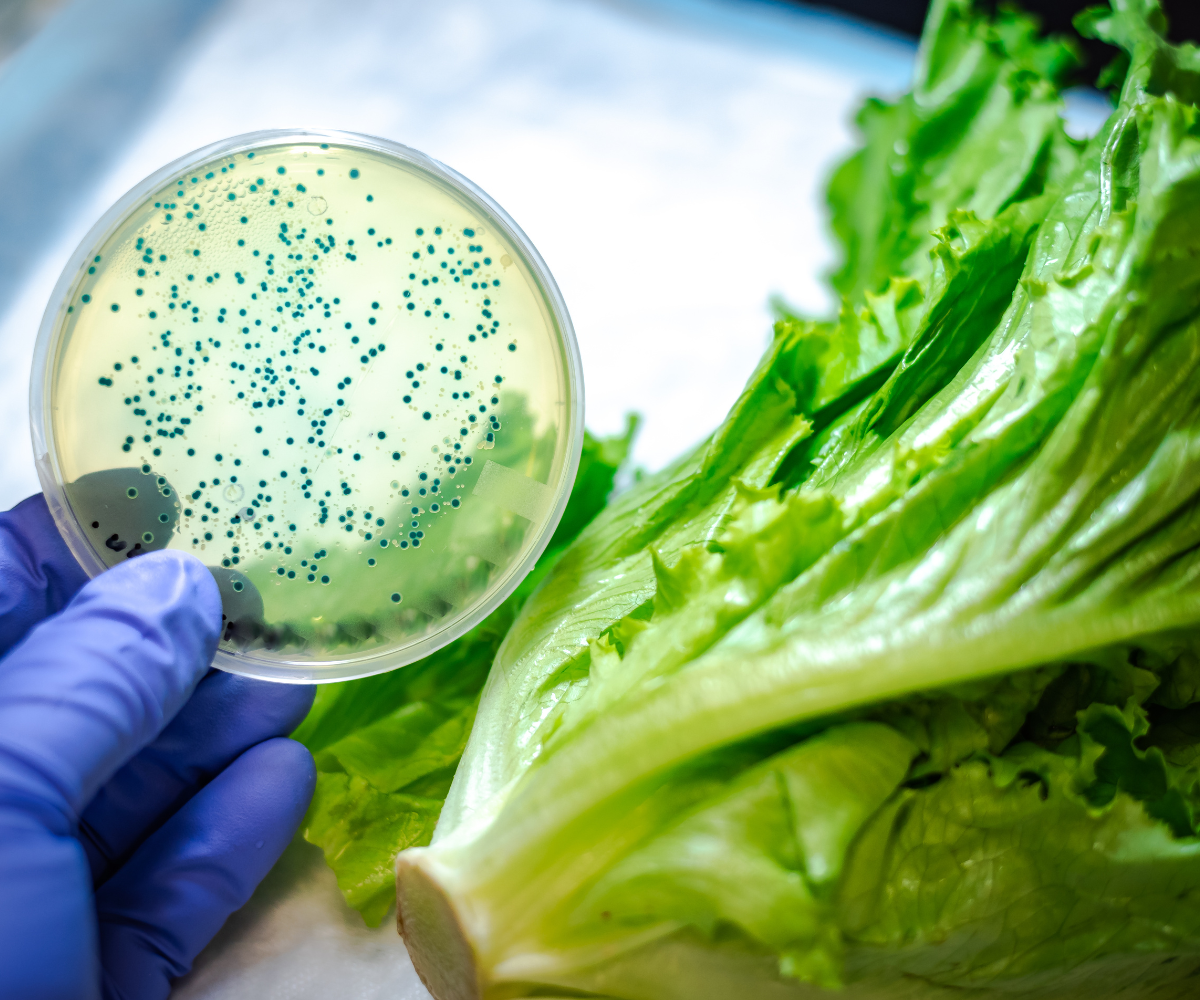
Introduction: Cross-contamination is one of the most significant threats to food safety, and it can occur at any stage of the food supply chain—from raw ingredient handling to final packaging. The spread of harmful pathogens such as Salmonella, Listeria and Coagulase Positive Staphylococcus can result in foodborne illnesses, product recalls, and damaged consumer trust. Understanding how cross-contamination occurs and taking proactive steps to prevent it is crucial for all food producers.
Body: Cross-contamination occurs when harmful microorganisms spread from one surface or food product to another. It can happen in many ways, including through raw food, improper handwashing, and contaminated equipment. A key example is when raw meat or poultry touches ready-to-eat foods, leading to the transfer of bacteria.
Prevention Tips:
- Separate Raw and Ready-to-Eat Foods: Always store and handle raw foods separately to prevent cross-contact with ready-to-eat items.
- Sanitize Surfaces and Equipment: Thoroughly clean and sanitize surfaces, utensils, and equipment between handling different foods.
- Educate Staff on Hygiene: Ensure that all employees follow strict handwashing and hygiene practices throughout the production process.
AML offers pathogen detection and surface hygiene testing to ensure that contamination risks are identified early, allowing you to act swiftly to prevent potential health hazards and product recalls.
Conclusion: Preventing cross-contamination is key to maintaining food safety and consumer health. Trust AML’s expert testing and monitoring services to help safeguard your products from harmful pathogens. Reach out to us today for assistance in improving your food safety practices!